.jpg)
Casting and Shaping of Precious Metals
Graphite is used in melting, casting and shaping of precious metals such as gold and silver, as well as in many areas due to its resistance to high temperature and thermal shocks.
What is Continuous Casting? What are Continuous Casting Methods and Advantages?
The process of solidifying the melted metal in the chamber in a certain cross-section with the help of a mould by cooling the area where solidification begins is called continuous casting process.
.jpg)
What is Graphite Crucible?
The chamber used in the melting of non-ferrous metals is called a crucible.
.jpg)
What are Graphite Usage Areas?
Due to its softness, it is used in pencil making and lubrication of moving metal parts, and due to its resistance to fire and acids, it is used in casting and refractory industry, crucible and laboratory materials.

What is Graphite?
Graphite, which has a crystalline structure just like diamond due to the carbon in its structure, is still a very soft material that cannot be compared to diamond in terms of hardness.
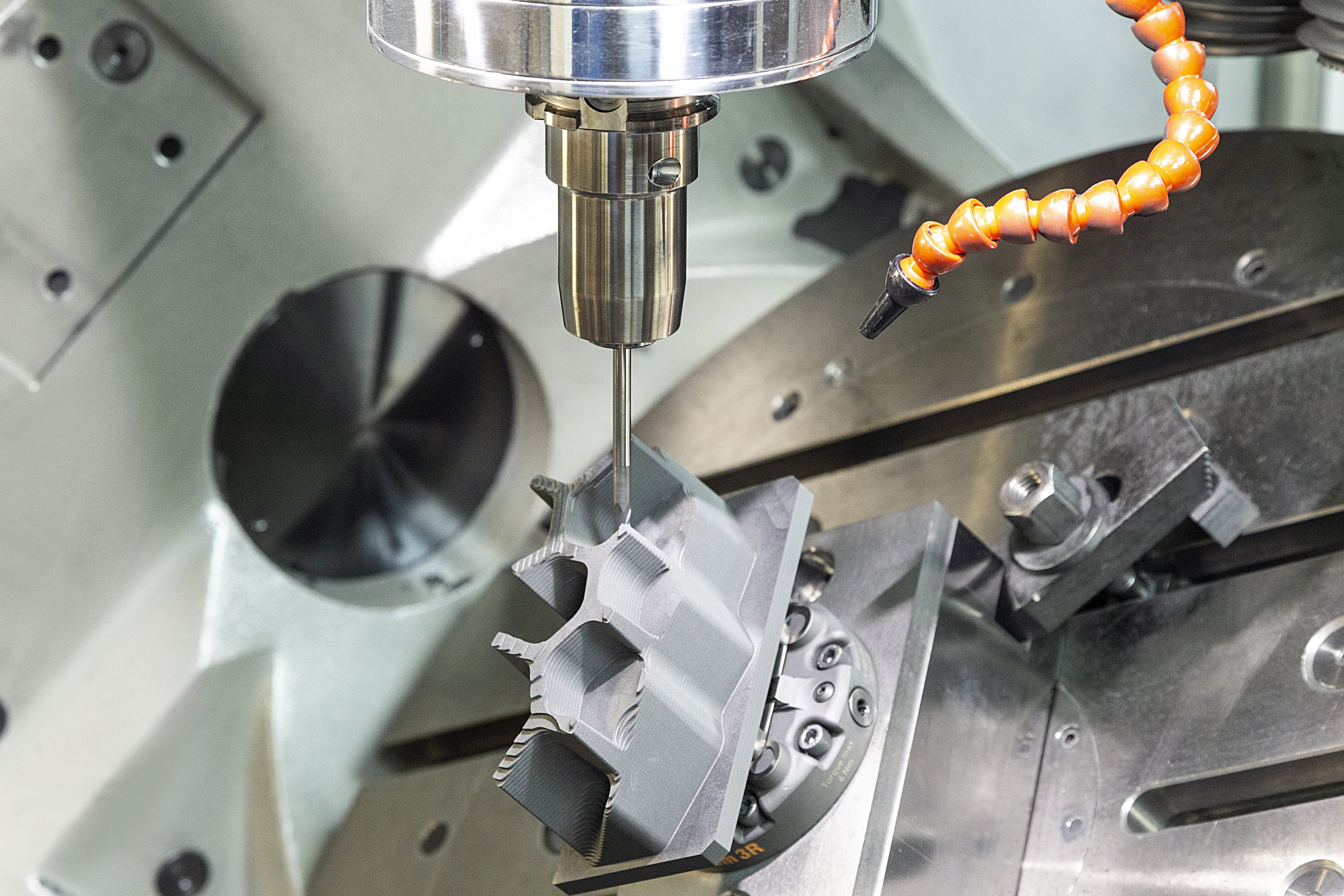

Graphite Electrode Replaces Copper in Plunge Erosion!
Especially preferred in the moulding sector, the process of shaping the workpiece by arc method by applying electric current to the conductive material is called plunge erosion method.

SKC Carbon Success in Carbon Graphite Products
Despite the difficult and fluctuating economic conditions of the 1970 - 90 period, MEGA (Schmidthammer Elektrokohle GmbH) regularly followed the developments in accordance with the technology of the day and realized the carbon-graphite raw material proces
Using the Latest Technology in Carbon Graphite Sector in Istanbul; SKC Karbon
SKC Karbon San. ve Tic A.Ş. offers high efficiency, precise graphite products to our customers in the fields of Electrical, Electronic and Mechanical applications with carbon and graphite materials in accordance with today's latest technologies and with o



